
Environment
- Environmental Policy
- Environmental Disclosure Initiatives in Line with the TCFD
- Environmental Data
- Environmental Issue Activities
Environmental Policy
The KANADEN Group, with the aim of handing over a clean planet to future generations, has positioned its Environmental Policy as one of its key management issues. For the development of a sustainable society, in all aspects of corporate activities, we strive to conserve and work in harmony with the global environment.
Environmental conservation activities
- (1)We will contribute to the development of a low carbon and recycle-oriented society by not only expanding the sales of eco-friendly products but also offering solutions that are perfect for our customers’ eco-business.
- (2)Our Group’s employees and families will work to promote energy savings, resource savings, and proper waste disposal to reduce the burden on the environment.
- (3)We will make a commitment to biodiversity-oriented environmental conservation activities to promote the coexistence of human beings and nature.
Compliance with environment-related laws and regulations
We will comply with environment-related laws and regulations, as well as outside environmental requirements the Group has agreed to.
Continuous improvement
We will work to develop an awareness of environmental conservation and to continuously improve and maintain initiatives that contribute to reducing the burden on the environment.
Goals and the company we want the KANADEN Group to become
- Procure electricity used in business activities from 100% renewable energy sources.
- Achieve zero emissions and carbon neutrality in business activities.
- Contribute to the creation of low carbon and recycle-oriented society by expanding renewable energy business and using energy conservation equipment.
Environmental Disclosure Initiatives in Line with the TCFD
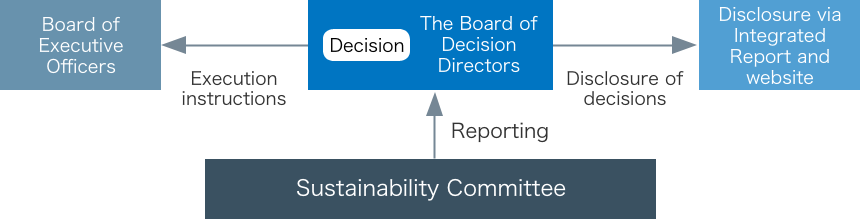
Governance
We are aware that addressing climate-related challenges is a material issue that will not only reduce business risks, but also lead to business opportunities.
With regard to overall sustainability initiatives, which include climate-related challenges, the Sustainability Committee, chaired by a Representative Director, formulates basic policies and strategies for the KANADEN Group’s initiatives, monitors the progress of such initiatives and reports its findings to the Board of Directors after investigating such challenges.
Upon receiving such reports, the Board of Directors appropriately deliberates on and determines policies and strategies relating to sustainability, including climate change.
Strategy
The Company endeavors to understand the impact of Climate change on Management of The Company and reflects the analyzed Risks and Opportunities in Business Strategy. In analyzing the business impact of Climate change, we conducted analyses on the transition of policies and market trends in each scenario (transition Risks and Opportunities) and physical changes (physical Risks and Opportunities) due to disasters, in order to grasp the medium-to long-term impacts, using the 1.5℃ scenario, which assumes a 1.5℃ increase in the global mean temperature by 2100 Years compared to before the industrial revolution, and the 4℃ scenario, which assumes a 4℃ increase. The base year is set as 2020, with the medium-term target set for 2030 and the long-term target aligned with the Paris Agreement's benchmark for 2050.
Reference scenario
| 1.5℃ scenario |
|
|---|---|
| 4℃ scenario |
|
Risks and Opportunities
We have identified the following items as the medium- to long-term risks and opportunities that climate change poses to the Company's operations. Extracted items are evaluated based on their importance (high, medium, low) using a two-axis approach considering occurrence probability and impact level. Our response to assessed risks and opportunities is aligned with materiality and our mid-term management plan, and we are advancing our initiatives with quantitative targets.
| Category | Risks and Opportunities Factors |
Business impact | Importance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risks | Transition Risks | Risks of Policies, Laws and Regulations |
|
|
High |
| Marketplace Risks |
|
|
High | ||
| Technology Risks |
|
|
Medium | ||
| Reputational Risks |
|
|
Medium | ||
| Physical Risks | Acute physical Risks |
|
|
High | |
| Chronic physical Risks |
|
|
Medium | ||
| Opportunities | Market | Enhance its own resource efficiency |
|
|
High |
| Changes in energy sources |
|
|
High | ||
| New products and services |
|
|
High | ||
| Strengthen resilience |
|
|
Medium | ||
Risk Management
With regard to Risks extracted based on scenario analyses, we conduct Organization across the entire company, Risk Management Committee, and Collaboration, and monitor Response status. The Board of Directors oversees integrated, high-priority company-wide risks, taking into account reports from the Sustainability Committee and Risk Management Committee, as well as other risks reported by each department. For more information about Risk Management Committee, see Risk Management section.
Indicators and targets
The Company consistently calculates its Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions. Our target figures aim to maintain the current figures.
Going forward, we will progress the improvement of our internal structure and supply chain adjustments, aimed toward Scope 3 measurements.
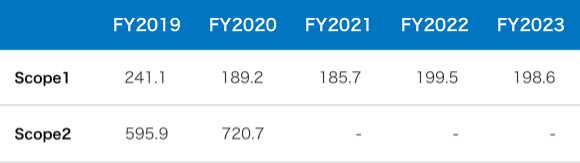
- (Notes) 1. Scope 1 emissions are calculated using gasoline consumption of company-owned vehicles. Scope 2 emissions are calculated using power and heat consumption of offices.
- 2. Electricity and heat consumption corresponding to Scope2(Market-based Method) emissions haves been set to “−” from FY2021 onward given that the Company has purchased the Certificate of Green Power and Heat.
Environmental Data
Electricity
We have been decreasing our power consumption and keeping it at low levels through measures that include replacing office lighting with LEDs.
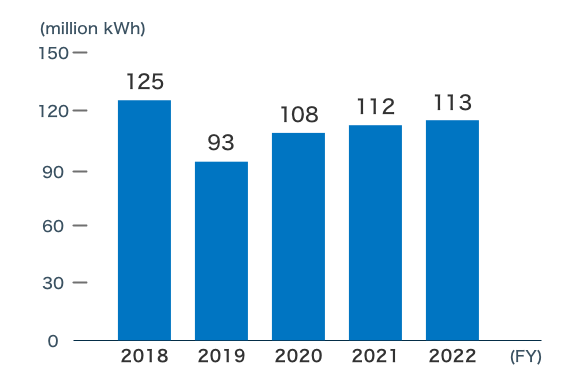
At Harumi Triton Square, to which our head office was relocated in 2019, we use electricity from an efficient district heating and cooling (DHC) system as a heat source for air conditioning.
What is DHC system?
The district heating and cooling (DHC) system involves effectively generating heat by producing hot and cold water for air conditioning at night in an underground district heating and cooling plant, and retaining it in large thermal storage tanks. The heat retained at night in the thermal storage tanks is then sent to the respective buildings during the day, and each of the air conditioning units evenly and carefully consumes the heat, which is conveyed using large temperature differences in the district heating network. As such, district heating and cooling accordingly saves energy by matching heat demand with manufacturing.
Copier paper
We have been promoting paperless operations and maintaining a low level of copy paper usage.
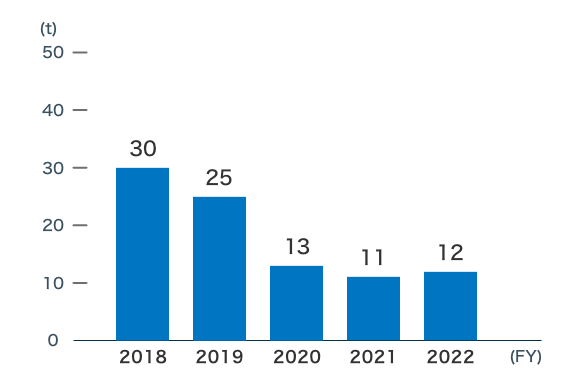
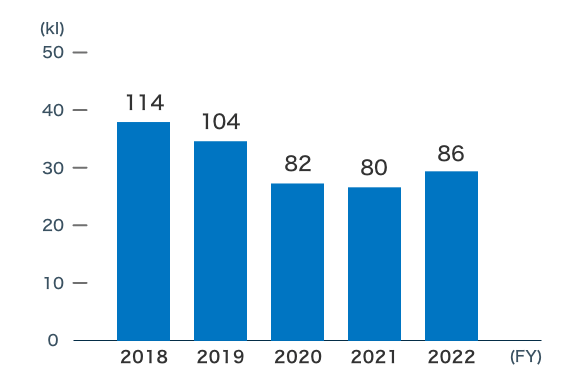
Gasoline
Gasoline usage has remained at a low level due to updated guidelines for vehicle introduction and the use of hybrid vehicles as standard equipment.
Environmental Issue Activities
Use of Green Energy
“Green energy” refers to environmentally-friendly electricity generated from renewable energy sources such as solar power, wind power, hydro power, biomass, and geothermal power. This is sustainable energy that does not emit CO2, which is one of the primary causes of global warming, at the time the electricity is generated, and contributes to reductions in energy use (reductions in consumption of fossil fuels).
In FY2024, the Company procured 1,030,000 kWh of electricity and 2,160,000 MJ of heat used at its business locations from green sources, in accordance with the guidelines set out by the Japan Quality Assurance Organization. We will continue to work to reduce our energy consumption and contribute to an environmentally friendly society by procuring green energy equivalent to the energy we consume.


Kigyo no Mori KANADEN
As part of Environmental conservation activities described in Environmental Policy, The KANADEN Group participates in the "Kigyo no Mori" project for promoting creation of low-pollen forests in the woodlands of Ome City, Tokyo.15 Years have passed since the tree planting, and we continue to contribute to the conservation of the environment.
Around 1,250 trees have been planted over an area of about 0.46 hectares, including broadleaf trees such as Japanese maples and oaks, and coniferous trees that produce less pollen, such as cedars and cypresses. 15 years have passed since the tree planting activities began in 2010, and the trees are growing well.

Environmental / energy business
Key measure
Expand business by mainly promoting promising products that contribute to reduction of environmental impacts
Principal products
- LED lighting
- Photovoltaic power generation systems
- Lithium-ion storage batteries
- Quick charger for electric vehicles
- Circular economy
- Electronic equipment for net-zero-energy buildings (ZEB)

Circular economy solutions
In FY2023, we jointly developed the low-temperature carbonization equipment for organic substances “KANA: Recircular,” which is a solution that will contribute to the circular economy.
This equipment produces carbon from food waste and sludge through thermal decomposition using a carbonization catalyst. The produced carbon can be used as a plastic substitute and soil improvement material, making it a system that contributes to the circular economy.
In addition, the reuse of food residues also has the effect of reducing industrial waste and curbing the CO2 emissions from disposing of them, thus helping to reduce the environmental burden and achieve the SDGs. We will accelerate our efforts to create new value, with the aim of contributing to the SDGs in the food industry and beyond.


